Anatomy and Physiology of Males and Females
Nov 28, 2024
Posted by:
Admin
The pinnacle of biological engineering is the human body. It has finely built structures and functions. There are
numerous similarities between the physiologies of males and females. Differences also exist. This increases their
distinct biological roles. Here, we will look at the physiological structure of men and women- the differences and
similarities between them.
An Overview of Human Physiological Structure
- Shared Anatomy: Males and females have the same basic physiological structure. They have the skeletal as well as circulatory systems
along with muscular and digestive systems functioning with several other such systems. They work together to support
life and maintain homeostasis.
- Distinct Anatomy: The reproductive and endocrine systems cause anatomical differences. Males have several organs. It includes the testes
and penis along with the prostate. Female glands include the ovaries, vagina along with fallopian tubes, and uterus.
These organs have specific functions in reproduction and hormone control.
Physiological Differences
- Strength and Muscle Mass:
Due to their higher testosterone levels, males typically have greater strength and muscle mass. However, females are
more equipped for flexibility and endurance, which are influenced by their hormonal composition.
- Bone Density:
Males have denser bones. Females are more prone to bone problems like osteoporosis, particularly after menopause , due to
their reduced estrogen levels.
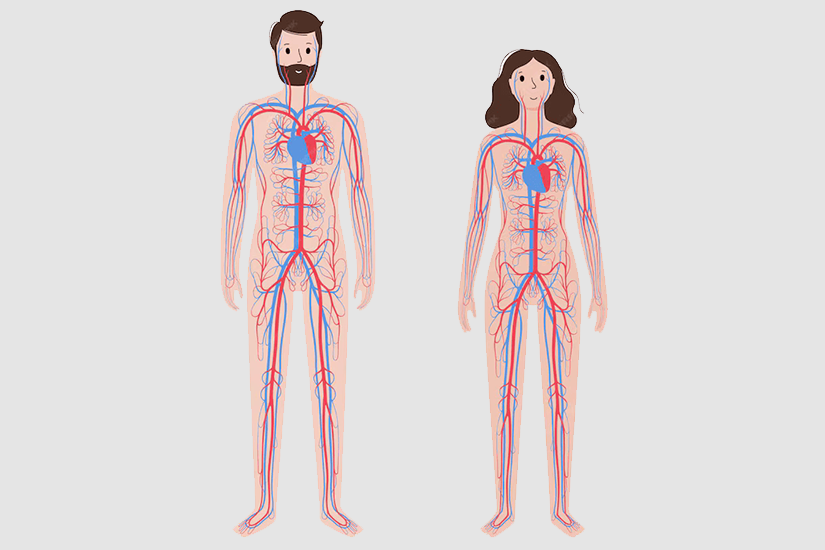
- Cardiovascular System:
The male heart is slightly larger than that of females. Males also have higher hemoglobin levels, which enhance oxygen
transport. Females, on the other hand, have a slightly quicker heart rate.
Reproductive Systems
- Male Reproductive System:
The male reproductive system produces and distributes sperm. The testes produce sperm and testosterone. Together, the
penis, vas deferens, epididymis, and accessory glands facilitate reproduction. It includes the prostate.
- Female Reproductive System:
The female reproductive system is made for ovulation and fertilization. It also cares for a growing fetus. The ovaries
produce eggs. They also produce the hormones progesterone and estrogen. The eggs are transported to the uterus through
the fallopian tubes upon fertilization. There they implant and develop. The vagina acts as a birth canal during
childbirth
Hormonal Differences
The hormones are greatly responsible for distinguishing male and female anatomy and physiology.
- The primary hormone in men is testosterone. It affects secondary sexual traits such as a deeper voice and facial hair.
They also affect bone density and muscle mass.
- Estrogen and progesterone are two hormones in females. They regulate menstruation. They also regulate reproductive
health and secondary characteristics like breast development.
Nonetheless, the pituitary gland and the hypothalamus regulate hormone secretion and preserve equilibrium in both sexes.
Conclusion
The physiology and anatomy of males and females define the unique and intricate design of the human body. While both
males and females share core similarities, their differences highlight the roles they play biologically. Understanding
the differences between the two not only highlights health and medicine. It also celebrates the diversity of human life.
Dr. Erande is one of the finest doctors who steps forward for all your sexual problems. If you are facing any issues,
you can always reach out to him before visiting anyone else.